HMRouter 简介
HMRouter 作为 HarmonyOS 的页面跳转场景解决方案,聚焦解决应用内原生页面的跳转逻辑。
HMRouter 底层对系统 Navigation 进行封装,封装了 Navigation、NavDestination、NavPathStack 的能力,提供了可复用的路由拦截、自定义转场动画、页面生命周期框架,目的是让开发者在开发中无需关注 Navigation、NavDestination 容器组件的相关细节及模板代码,更好的进行模块间解耦。
特性
基于注解声明路由信息
支持 Har、Hsp、Hap
支持 Navigation 路由栈嵌套
支持路由拦截器(包含全局拦截、单页面拦截、跳转时一次性拦截)
支持生命周期回调(包含全局生命周期、单页面生命周期、跳转时一次性生命周期)
内置转场动画(页面、Dialog),可配置方向、透明度、缩放,支持跟手抽屉式转场动画,同时支持配置某个页面的转场动画、跳转时的一次性动画
支持 Dialog 类型页面、支持单例页面
依赖版本
HarmonyOS NEXT Beta3 及以上
使用方法
1. 打开允许权限
# 在模块的module.json5文件中配置网络权限
{
"module":{
"requestPermissions": [
{
"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"
}
],
}
}2. 安装依赖
ohpm install @hadss/hmrouter3. 使用配置
- (1) 修改项目的 hvigor/hvigor-config.json 文件,加入路由编译插件(根目录)
{
"dependencies": {
"@hadss/hmrouter-plugin": "^1.0.0-rc.3" // 你自己的版本号必须和oh-package.json5的版本号一致
},
// ...其他配置
}- (2) 在模块中引入路由编译插件,修改
hvigorfile.ts
这里的文件是在模块下面 就是 Entry 下面的hvigorfile.ts
而不是根目录下的hvigorfile.ts
import { hapTasks } from "@ohos/hvigor-ohos-plugin";
import { hapPlugin } from "@hadss/hmrouter-plugin";
export default {
system: hapTasks,
plugins: [hapPlugin()],
};INFO
如果是 Har 则使用 harPlugin(), Hsp 则使用 hspPlugin()
初始化
- (1) 在模块的
entry/src/main/ets>entryability>entryAbility.ets中初始化 HMRouter
import { HMRouterMgr } from "@hadss/hmrouter";
// 初始化 HMRouter
onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam): void {
hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'Ability onCreate');
HMRouterMgr.init({
context: this.context
})
}- (2) 工程目录下的 build-profile.json5 中,配置 useNormalizedOHMUrl 属性为 true
{
"app": {
"products": [
{
"name": "default",
"signingConfig": "default",
"compatibleSdkVersion": "5.0.0(12)",
"runtimeOS": "HarmonyOS",
"buildOption": {
"strictMode": {
"useNormalizedOHMUrl": true
}
}
}
],
// ...其他配置
}
}初级使用
使用的时候只能在虚拟机上运行,不能在预览器运行
(1) 创建三个页面
Index.ets (路由入口页面)
Index2.ets (跳转页面)
Index3.ets (跳转页面)
(2) Index.ets 路由入口页面
import { HMDefaultGlobalAnimator, HMNavigation, HMRouterMgr } from '@hadss/hmrouter';
import { AttributeUpdater } from '@kit.ArkUI';
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = 'Hello World';
modifier: AppNavModifier = new AppNavModifier();
build() {
Column() {
// 使用HMNavigation容器
HMNavigation({
navigationId: 'AppNavigation', options: {
standardAnimator: HMDefaultGlobalAnimator.STANDARD_ANIMATOR,
dialogAnimator: HMDefaultGlobalAnimator.DIALOG_ANIMATOR,
modifier: this.modifier
}
}){
Button("点击跳转到2").fontSize(62).onClick(()=>{
HMRouterMgr.push({
pageUrl:'Index2'
})
})
}
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
}
}
class AppNavModifier extends AttributeUpdater<NavigationAttribute> {
initializeModifier(instance: NavigationAttribute): void {
instance.mode(NavigationMode.Stack);
instance.navBarWidth('100%');
instance.hideTitleBar(true);
instance.hideToolBar(true);
}
}(3) Index2.ets 跳转页面(页面必须导出否则报错)
import { HMRouter, HMRouterMgr } from '@hadss/hmrouter';
// 必须导出 必须里面写pageUrl
@HMRouter({pageUrl:'Index2'})
@Entry
@Component
export struct Index2 {
build() {
Column(){
Button("点击2").type(ButtonType.Capsule).onClick(()=>{
HMRouterMgr.push({
navigationId:'AppNavigation',
pageUrl:'Index3'
})
})
}
}
}(4) Index3.ets 跳转页面(页面必须导出否则报错)
import { HMRouter, HMRouterMgr } from '@hadss/hmrouter'
@HMRouter({pageUrl:'Index3'})
@Entry
@Component
export struct Index3 {
build() {
Column(){
Button("点击3").type(ButtonType.Capsule).onClick(()=>{
console.log("点击了我3")
HMRouterMgr.push({
navigationId:'AppNavigation',
pageUrl:'Index2'
})
})
}
}
}跳转
push
- 压入栈,如果栈中存在则不压入
HMRouterMgr.push(
{
navigationId: "AppNavigation", // 操作页面栈(你自己的ID),当navigationId为空时,表示对最近一次操作的navigation进行路由跳转
pageUrl: "Index2", // 需要跳转的目标页面,push/replace操作必填参数
param: {
data: { name: "第一个页面过来的数据", id: 1 },
}, //跳转页面携带参数,push/replace表示传递给下个页面的参数,pop表示回传给上一个页面的返回参数
interceptors: [], // IHMInterceptor[] 自定义拦截器,最高优先级执行
animator: false, // IHMAnimator | boolean 自定义动画,使用传入的动画进行专场,不再使用原先定义的转场动画,传入false时将禁用动画
skipAllInterceptor: false, // // 是否跳过所有拦截器执行,不能跳过传入的interceptors拦截器
},
{
// 页面返回回调,最好用箭头函数因为要改变外面的状态值
onResult: (popInfo: HMPopInfo) => {
console.log(JSON.stringify(popInfo));
},
// // 目标页面跳转完成回调
onArrival: () => {
console.log("页面跳转过去了,已经完成了");
},
// 目标页面找不到回调
onLost: () => {
console.log("没有这个页面啊");
},
}
);- 接收参数
this.param = HMRouterMgr.getCurrentParam();
Text(this.param).fontSize(62);replace
参数同 push 只不过他是替换栈顶的页面
pop(不一样)
如需使用页面返回功能,在对应的业务逻辑位置使用 HMRouterMgr 提供的 pop 方法实现页面返回,同样的 pop 方法支持传入 navigationId,同时 HMRouter 还支持在返回时通过配置 param 参数向其所返回的页面传递参数。
他接收两个参数一个就是返回页面的信息
另外那个是层级(本人测试没有效果)
// @param pathInfo
// @param skipedLayerNumber 页面返回的层级数量,默认为0,表示返回上一级,1表示跳过一级页面返回,
// 即同时两个页面出栈,pathInfo.pathInfo参数优先级高于skipedLayerNumber
HMRouterMgr.pop({
navigationId: "mainNavigationId",
pageUrl: "HomePage",
param: this.param,
});- pop 接收参数 一定要写到 onResult 回调函数里面 它里面在改变状态
Button("点击2").type(ButtonType.Capsule).onClick(() => {
console.debug("测试路由", JSON.stringify(this))
HMRouterMgr.push({
navigationId: 'AppNavigation',
pageUrl: 'Index3'
}, {
// 页面返回回调
onResult: (popInfo: HMPopInfo) => {
console.debug("测试路由", JSON.stringify(this))
console.debug("测试路由", JSON.stringify(popInfo.result))
this.routerId = (popInfo.result as ParamsType).id;
console.debug("测试路由", this.routerId)
if (this.routerId == 4) {
console.debug("测试路由", "this.routerId确实等于3")
console.debug("测试路由结果", JSON.stringify(this))
this.flag = true;
this.name = (popInfo.result as ParamsType).name;
}
},
// // 目标页面跳转完成回调
onArrival() {
console.log("页面跳转过去了,已经完成了")
},
// 目标页面找不到回调
onLost() {
console.log("没有这个页面啊")
}
})
})- 多次页面跳转返回指定页面
当页面跳转路径如 HomePage->PageA->PageB->PageC,开发者希望在 PageC 的页面逻辑中直接返回到 HomePage 并携带参数,开发者仅需使用 HMRouterMgr 提供的 pop 方法,传入要返回目标页面的 pageUrl、传递的参数 param,即可直接带参返回到指定页面。
HMRouterMgr.pop({
navigationId: "mainNavigationId",
pageUrl: "HomePage",
param: this.param,
});
生命周期
(1) 创建生命周期钩子函数
在 entry>src>main>etc 下面新建一个 Lifecycle 文件夹,在 Lifecycle 文件夹下面新建一个 Lifecycle.ets 文件,Lifecycle.ets 文件内容如下:
import { HMLifecycle, HMLifecycleContext, IHMLifecycle } from "@hadss/hmrouter";
@HMLifecycle({ lifecycleName: "RouterLife" })
export class RouterLife implements IHMLifecycle {
onPrepare(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onPrepare");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onPrepare",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onAppear(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onAppear");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onAppear",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onDisAppear(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onDisAppear");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onDisAppear",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onShown(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onShown");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onShown",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onHidden(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onHidden");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onHidden",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onWillAppear(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onWillAppear");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onWillAppear",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onWillDisappear(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onWillDisappear");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onWillDisappear",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onWillShow(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onWillShow");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onWillShow",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onWillHide(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onWillHide");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onWillHide",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onReady(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): void {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onReady");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onReady",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
}
onBackPressed(ctx: HMLifecycleContext): boolean {
console.debug("测试路由生命周期", "RouterLife", "onBackPressed");
console.debug(
"测试路由生命周期",
"RouterLife",
"onBackPressed",
JSON.stringify(ctx)
);
return false;
}
}(2) 页面上使用生命周期函数
- 在需要的页面中引入生命周期
我这里拿一个基础页面举例子,要在 HMrouter 里面加入 lifecycle,名字就是你定义的生命周期类名
import { HMLifecycle, HMPopInfo, HMRouter, HMRouterMgr } from '@hadss/hmrouter';
// 必须导出 必须里面写pageUrl
@HMRouter({ pageUrl: 'Index2', lifecycle: 'RouterLife' })
@Entry
@Component
export struct Index2 {
@State routerId: number = 0;
@State flag: boolean = false;
@State name: string = ""
build() {
Column() {
if (this.flag) {
Text("收到了返回值").fontSize(67)
Text(this.name).fontSize(72)
}
Button("点击2").type(ButtonType.Capsule).onClick(() => {
console.debug("测试路由", JSON.stringify(this))
HMRouterMgr.push({
navigationId: 'AppNavigation',
pageUrl: 'Index3'
}, {
// 页面返回回调
onResult: (popInfo: HMPopInfo) => {
console.debug("测试路由", JSON.stringify(this))
console.debug("测试路由", JSON.stringify(popInfo.result))
this.routerId = (popInfo.result as ParamsType).id;
console.debug("测试路由", this.routerId)
if (this.routerId == 4) {
console.debug("测试路由", "this.routerId确实等于3")
console.debug("测试路由结果", JSON.stringify(this))
this.flag = true;
this.name = (popInfo.result as ParamsType).name;
}
},
// // 目标页面跳转完成回调
onArrival() {
console.log("页面跳转过去了,已经完成了")
},
// 目标页面找不到回调
onLost() {
console.log("没有这个页面啊")
}
})
})
}
}
}
interface ParamsType {
id: number,
name: string,
}(3) 结果
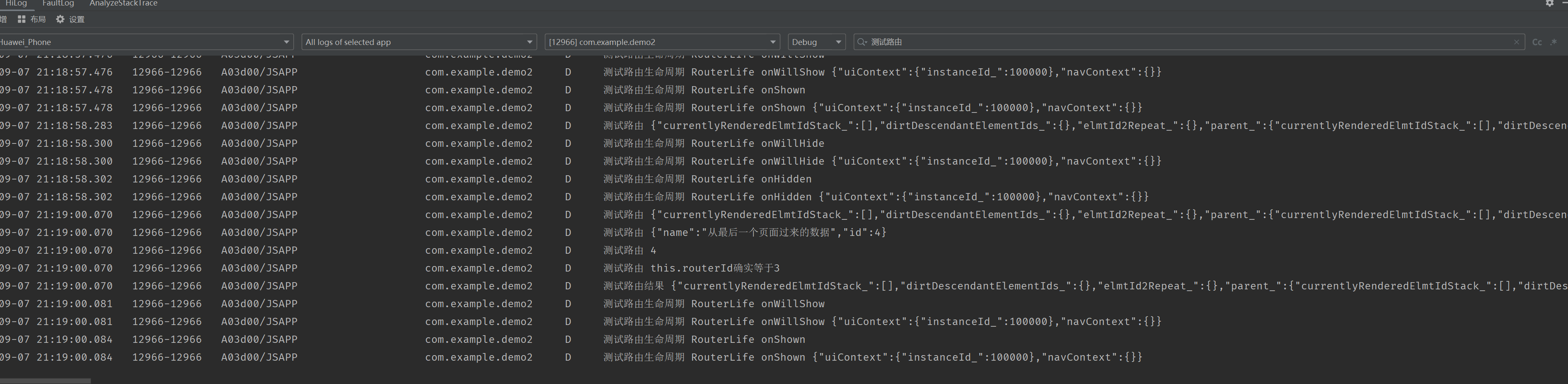
拦截器
创建拦截器
- (1) 在 entry>src>main>stc>model(你自己起的一个文件夹)新建 Interceptor.ets 文件
INFO
HMInterceptor 是拦截器装饰器 里面有三个参数
- nterceptorName: string, 拦截器名称,必填
- priority: number, 拦截器优先级,数字越大优先级越高,非必填,默认为 9;
- global: boolean, 是否为全局拦截器,当配置为 true 时,所有跳转均过此拦截器;默认为 false,当为 false 时需要配置在@HMRouter 的 interceptors 中才生效。
我在下面创建了 2 个拦截器 它优先执行 priority 为 9 的,在执行 priority 为 7 的
import { HMInterceptor, HMInterceptorAction, HMInterceptorInfo, HMRouterMgr, IHMInterceptor } from '@hadss/hmrouter';
@HMInterceptor({priority:9,interceptorName:'LoginInterceptor'})
export class LoginInterceptor implements IHMInterceptor {
private isLogin: boolean = true;
handle(info: HMInterceptorInfo): HMInterceptorAction {
if (this.isLogin) {
// 跳转下一个拦截器处理
console.debug("测试拦截",'拦截器1','拦截住了');
return HMInterceptorAction.DO_NEXT;
} else {
HMRouterMgr.push({
pageUrl: 'Index4',
param: { targetUrl: info.targetName },
skipAllInterceptor: true
})
// 拦截结束,不再执行下一个拦截器,不再执行相关转场和路由栈操作
return HMInterceptorAction.DO_REJECT;
}
}
}
@HMInterceptor({priority:7,interceptorName:'LoginInterceptor2'})
export class LoginInterceptor2 implements IHMInterceptor {
private isLogin2: boolean = true;
handle(info: HMInterceptorInfo): HMInterceptorAction {
if (this.isLogin2) {
// 跳转下一个拦截器处理
console.debug("测试拦截",'拦截器2','拦截住了');
return HMInterceptorAction.DO_NEXT;
} else {
HMRouterMgr.push({
pageUrl: 'Index4',
param: { targetUrl: info.targetName },
skipAllInterceptor: true
})
// 拦截结束,不再执行下一个拦截器,不再执行相关转场和路由栈操作
return HMInterceptorAction.DO_REJECT;
}
}
}
动画
全局动画
- (1) 创建自定义动画 entry>src>main>ets>model(自己定义的文件夹)>(新建的 HMAnimator)
import { IHMAnimator } from "@hadss/hmrouter";
export const globalPageTransitionEffect: IHMAnimator.Effect =
new IHMAnimator.Effect({
direction: IHMAnimator.Direction.BOTTOM_TO_TOP,
opacity: { opacity: 0.5 },
scale: { x: 0.5, y: 0.2 },
});- (2) 挂载到全局
import { globalPageTransitionEffect } from "../model/HMAnimator";
HMNavigation({
navigationId: "AppNavigation",
options: {
standardAnimator: globalPageTransitionEffect,
dialogAnimator: HMDefaultGlobalAnimator.DIALOG_ANIMATOR,
modifier: this.modifier,
},
});特殊页面 自定义动画
开发者可以自定义动画类并实现 IHMAnimator 接口中的 effect 方法
该方法会将页面进出场的效果对象 enterHandle 与 exitHandle 作为参数传入
可通过参数对象上的 start、finish 方法,设置对应效果的起止状态,支持设置的常用属性还有:
curve:设置动画速度曲线,支持通过 Curve 枚举传入值,默认 Curve.EaseInOut。
duration:动画持续时长,单位 ms。
INFO
start/finish 方法参数说明如下:
translateOption:坐标位置,以屏幕左上角为原点,水平向右为 x 轴正方向,竖直向下为 y 轴正方向。百分比相对于屏幕宽度。例如希望从右侧进入可以设置 translateOption.x 从 100%变到 0。
scaleOption:页面缩放,可通过 scaleOption.x、scaleOption.y 单独设置横纵方向的缩放比例。
opacityOption:跳转页面的透明度
以下代码示例表示入场时由屏幕底部以线性速度向屏幕顶部运动,入场动画持续时长为 3000ms。
出场时从屏幕顶部以线性速度向屏幕底部运动,出场动画持续时长也为 3000ms。
流程
(1) 创建自定义动画 entry>src>main>ets>model(自己定义的文件夹)>(新建的 HMCustomAnimator)
import {
HMAnimator,
HMAnimatorHandle,
IHMAnimator,
OpacityOption,
ScaleOption,
TranslateOption,
} from "@hadss/hmrouter";
@HMAnimator({ animatorName: "CustomAnimator" })
export class CustomAnimator implements IHMAnimator {
effect(enterHandle: HMAnimatorHandle, exitHandle: HMAnimatorHandle): void {
// 入场动画
enterHandle.start(
(
translateOption: TranslateOption,
scaleOption: ScaleOption,
opacityOption: OpacityOption
) => {
translateOption.y = "100%";
scaleOption.x = 0.7;
opacityOption.opacity = 0.3;
}
);
enterHandle.finish(
(
translateOption: TranslateOption,
scaleOption: ScaleOption,
opacityOption: OpacityOption
) => {
translateOption.y = "0";
scaleOption.x = 1;
opacityOption.opacity = 1;
}
);
enterHandle.duration = 3000;
enterHandle.curve = Curve.Linear;
// 出场动画
exitHandle.start(
(
translateOption: TranslateOption,
scaleOption: ScaleOption,
opacityOption: OpacityOption
) => {
translateOption.y = "0";
scaleOption.x = 1;
opacityOption.opacity = 1;
}
);
exitHandle.finish(
(
translateOption: TranslateOption,
scaleOption: ScaleOption,
opacityOption: OpacityOption
) => {
translateOption.y = "100%";
scaleOption.x = 0.7;
opacityOption.opacity = 0.3;
}
);
exitHandle.duration = 3000;
enterHandle.curve = Curve.Linear;
}
}(2) 要跳转到的页面使用
import { CustomAnimator } from "../model/HMCustomAnimator";
Button("点击3")
.type(ButtonType.Capsule)
.onClick(() => {
console.log("点击了我3");
HMRouterMgr.push({
navigationId: "AppNavigation",
pageUrl: "Index4",
animator: new CustomAnimator(),
});
});依据条件来执行不同的动画
- 比如说横屏一个动画 效果 竖屏一个动画效果
简单来说就是通过判断,横屏一个自定义动画,竖屏就走另外一个动画
@Component
export struct CommentInput {
// ...
build() {
Row() {
// ...
Image($r('app.media.icon_comments'))
.width(24)
.height(24)
.margin({ right: 16 })
.onClick(() => {
if (this.isLandscape) {
HMRouterMgr.push({
navigationId: this.queryNavigationInfo()?.navigationId,
pageUrl: 'liveComments',
param: {
commentRenderNode: this.commentRenderNode,
},
animator: myAnimator2
}, {
onResult: (paramInfo: PopInfo) => {
this.videoWidth = '100%';
}
})
this.videoWidth = '50%';
} else {
HMRouterMgr.push({
navigationId: this.queryNavigationInfo()?.navigationId,
pageUrl: 'liveComments',
param: {
commentRenderNode: this.commentRenderNode,
},
animator: myAnimator1
}, {
onResult: (paramInfo: PopInfo) => {
this.videoHeight = '100%'
}
})
this.videoHeight = '30%'
}
})//
})// ...
}
// ...
}
}